
A falange of imperial eagle with marks of court from Cave Foradada. Credit: Antonio Rodríguez-Hidalgo
Eagle talons are regarded as the first elements used to make jewellery by Neanderthals, a practice which spread around Southern Europe about 120,000 to 40,000 years ago. Now, for the first time, researchers found evidence of the ornamental uses of eagle talons in the Iberian Peninsula. An article published on the cover of the journal Science Advances talks about the findings, which took place in the site of the Cave Foradada in Calafell. The study was led by Antonio Rodríguez-Hidalgo, researcher at the Institute of Evolution in Africa (IDEA) and member of the research team in a project of the Prehistoric Studies and Research Seminar (SERP) of the UB.
The interest in these findings lies in the fact that it is the most modern piece of the kind so far regarding the Neanderthal period and the first one found in the Iberian Peninsula. This finding widens the temporal and geographical limits that were estimated for these kind of Neanderthal ornaments. This would be "the last necklace made by the Neanderthals," according to Antonio Rodríguez-Hidalgo.
"Neanderthals used eagle talons as symbolic elements, probably as necklace pendants, from the beginnings of the mid Palaeolithic," notes Antonio Rodríguez-Hidalgo. In particular, what researchers found in Cova Foradada are bone remains from a Spanish Imperial Eagle (Aquila Adalberti), from more than 39,000 years ago, with some marks that show these were used to take the talons so as to make pendants. The remains correspond to the left leg of a big eagle. By the looks of the marks, and analogy regarding remains from different prehistorical sites and ethnographic documentation, researchers determined that the animal was not used for consumption but for symbolic reasons. Eagle talons are the oldest ornamental elements known in Europe, even older than the seashells Homo sapiens sapiens perforated in northern Africa.
The findings belong to the Châtelperronian culture, typical of the last Neanderthals that lived in Europe, and coinciding with the moment when this species came in contact with Homo sapiens sapiens from Africa and expanding through the Middle East.
Juan Ignacio Morales, researcher in the program Juan de la Cierva affiliated at SERP and an author of the article, suggests that this use of eagle talons as ornaments could have been a cultural transmission from the Neanderthals to modern humans, who adopted this practice after reaching Europe.
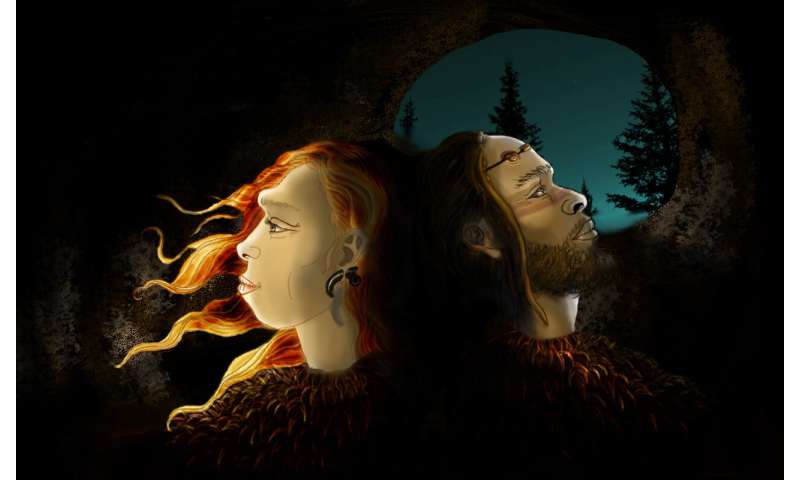

Idealized reconstruction of Neanderthals and Sapiens, the two human populations that inhabited Cova Foradada, wearing personal ornaments. Credit: Lou-Octavia Mørch
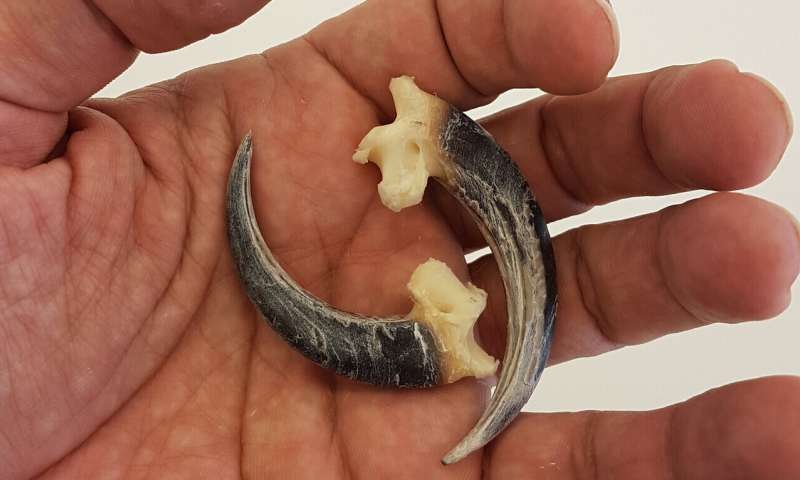
Imperial eagle talons. Credit: Antonio Rodríguez-Hidalgo
Cova Foradada covers the most meridional Châtelperronian culture site in Europe. The discovery involved a change in the map of the territory where the shift from Middle Palaeolithic to Upper Palaeolithic took place 40,000 years ago, and where interaction between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens sapiens probably took place.
Studies in Cova Foradada started in 1997. At the moment, the supervision of the excavation is led by Juan Ignacio Morales and Artur Cebrià. The archaeological study of this site is included in a SERP project funded by the Department of Culture of the Catalan Government and another funded by the Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, headed by UB professor and SERP director Josep M Fullola.
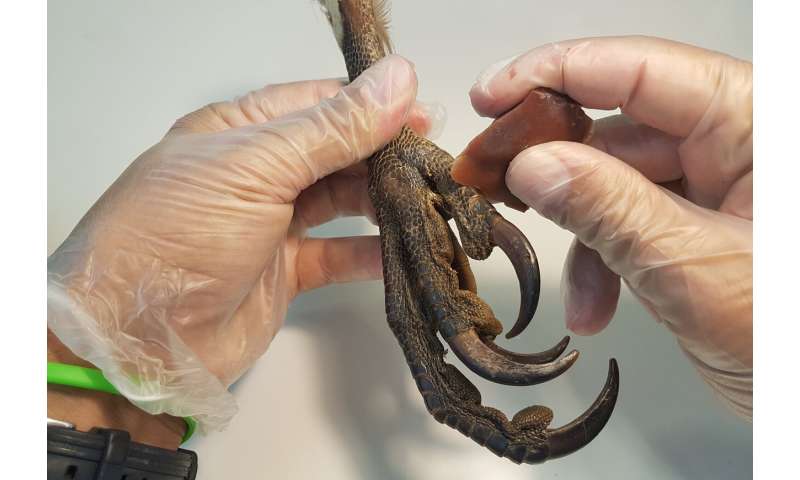

Experimental butchering of vulture talons to stablish analogies with archaeological cut marks. Credit: Antonio Rodríguez-Hidalgo
The first author of the article in Science Advances is Antonio Rodríguez Hidalgo, from the Institute of Evolution in Africa (IDEA). Other participants, apart from SERP members, are the researchers from Rovira i Virgili University, the Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution (IPHES), the Natural History Museum of Paris, the University of Salamanca, the University of Calgary (Canada) and the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS).
More information:
A. Rodríguez-Hidalgo at IDEA (Instituto de Evolución en África) in Madrid, Spain el al., "The Châtelperronian Neanderthals of Cova Foradada (Calafell, Spain) used imperial eagle phalanges for symbolic purposes," Science Advances (2019). advances.sciencemag.org/content/5/11/eaax1984
Citation:
The last Neanderthal necklace (2019, November 1)
retrieved 1 November 2019
from https://phys.org/news/2019-11-neanderthal-necklace.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
#Biology | https://sciencespies.com/biology/the-last-neanderthal-necklace/
No comments:
Post a Comment